By mainstreaming gender equality and inclusivity, this initiative not only seeks to drive scientific excellence but also foster equitable and inclusive growth across the continent.
Africa holds immense potential for global scientific and technological advancements. However, unlocking this potential requires a paradigm shift - one that embraces collaboration, inclusivity, and sustainability.
For this reason, ACTS is implementing a project that aims to strengthen the capacity of Science Granting Councils (SGCs) in Sub-Sahara Africa (SSA) to fund and manage research and innovation projects in areas aligned with their national development plans that integrate inclusivity and sustainability. Specifically, this initiative aims to refine and adapt research and innovation frameworks to meet the unique needs of African countries, support the design and management of high-quality research competitions, and ensure the seamless execution of projects through robust partnerships.
By mainstreaming gender equality and inclusivity, this initiative not only seeks to drive scientific excellence but also to foster equitable and inclusive growth across the continent.
Currently, the initiative is supporting 17 SGCs to implement more than 80 research and innovation projects across the continent. The initiative has made deliberate efforts to enhance inclusion of early career researchers, private sector actors, small and medium-sized enterprises, and community actors. Interestingly, all councils have committed increased resources and surpassed their pledges (At least USD $740,909 or 12% of total RIM project budget) which is more than 10% that most councils promised. In 2023,a total of USD$ 1,245,655.98 was disbursed to support projects across the 17 councils while USD$ 1,012,013.72was disbursed in 2024.
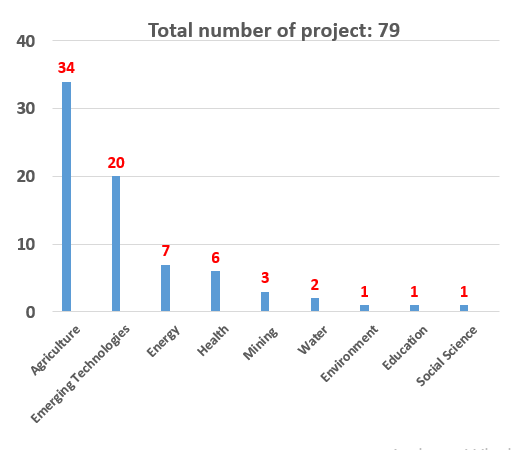
Number of projects implemented per sector under the RIM project.
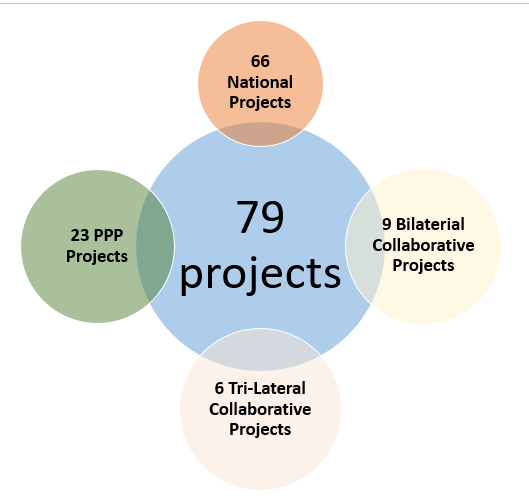
In total, councils have selected 79 research and innovation projects for funding. Out of these 66 projects are national while 15 projects are collaborative projects - 9 bilateral projects and 6 tri-lateral projects. There are also 23 public-private partnership projects. Agriculture and emerging technologies are the most preferred sectors by Councils,with energy, health and mining being amongst the five top sectors. Emerging technologies are rapidly gaining interest of the councils. Out of 79 projects selected by councils,emerging technologies account for 20 projects translating to25 % of the total projects being funded by the councils.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
There is a steady appreciation by the councils of the need to invest public resources to stimulate collaborations between academia-industry through funding PPP projects. Working with industries to co-create and implement projects is thesurest way of enhancing uptake of solutions developed by the academia by industry. Out of 79 projects selected by councils, 23 projects (29%) are Public Private Partnership Projects. At least 10 of the 16 councils (i.e. 63% of the councils) are funding PPP projects. Based on the above categorization, 9 RIM research PPP projects are at the ideation stage; 8 projects at the testing stage and 6 projects fall under the stage of adoption and uptake.
The private entities that form part of PPP arrangements under the RIM project are mainly private companies, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs), innovation hubs, science/technology parks and agricultural producer organisations.

